Squadron 42 Monthly Report: December 2018
This is a cross-post of the report that was recently sent out via the monthly Squadron 42 newsletter. We’re publishing this a second time as a Comm-Link to make it easier for the community to reference back to, and plan on following this process for future Squadron 42 Monthly Reports.
Attention Recruits,
What you are about to read is the latest information on the continuing development of Squadron 42.
Read on for pertinent details from our planet-wide operations on Squadron 42-related work over the last month, as well as intel on an exciting new dispatch. The information contained in this communication is extremely sensitive and it is of paramount importance that it does not fall into the wrong hands. Purge all records after reading.
Over and out,
UEE Naval High Command
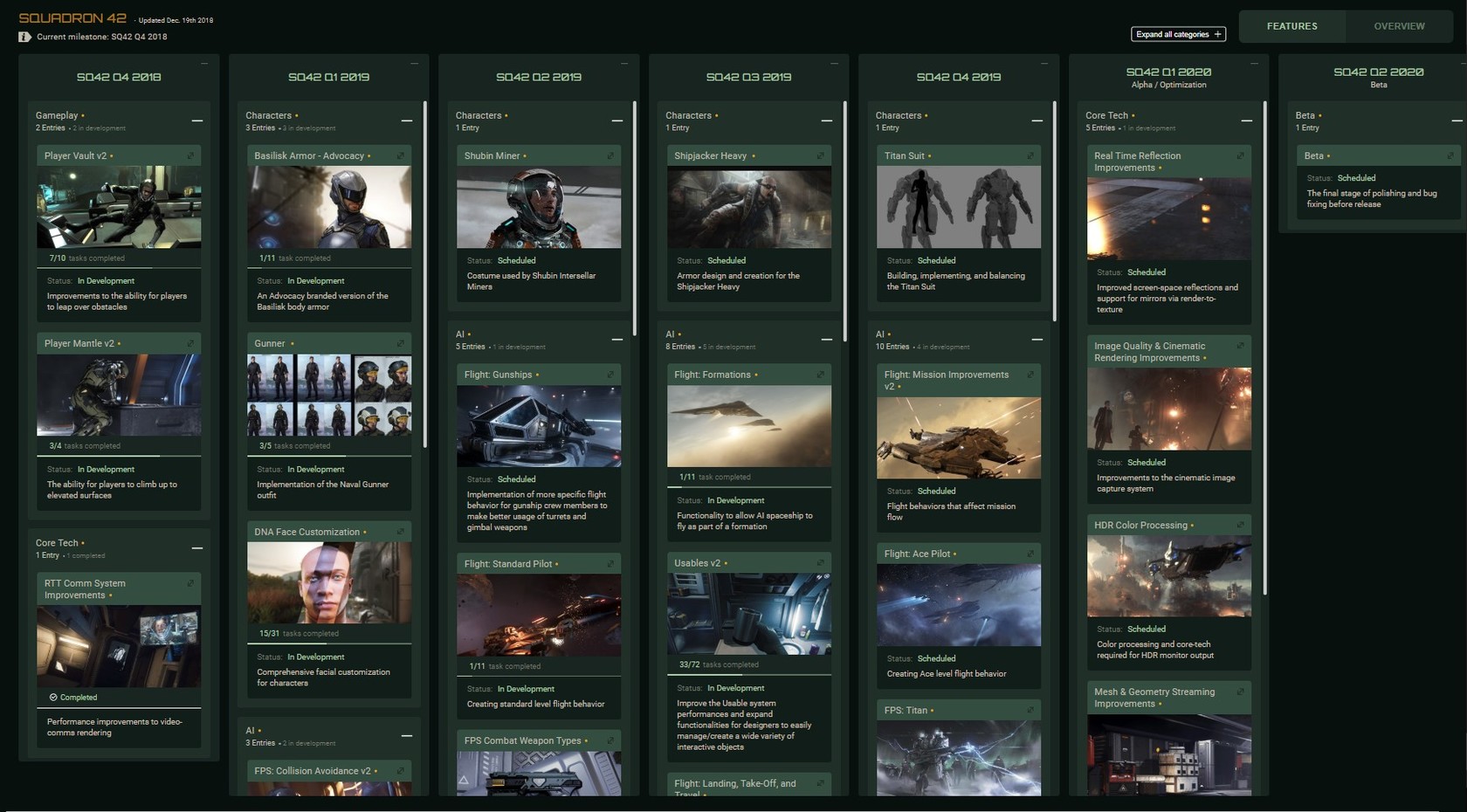
The Road to Glory
Today sees the unveiling of our Squadron 42 roadmap, a useful piece of intel that tracks the progress of development in detail. Much like the Persistent Universe roadmap, this is linked to our JIRA tracking system, and thus lets you see at a glance the work remaining on the game as we thunder on toward the finish line. Of course, also like its Star Citizen counterpart, the Squadron 42 roadmap is not necessarily exhaustive and may be changed or updated as development continues. Make sure you read the caveats, and enjoy this insight into the process.
This monthly project update will work as something of a companion piece, shedding more light on specific work done by each development team, while the roadmap will provide dynamic real-time tracking of progress weekly.
Without further adiue, let’s see what the devs fighting the good fight on the frontlines have been up to…
AI
This month, Ship AI’s focus was on optimizing the Tactical Point System. They now have multiple queries bundled together in a batch from different threads, which allows more control over the cost of the overall system. They submitted several optimizations for the character movement system, which can now update all the components in a multithreaded batch approach and will utilize the maximum the CPU resources during the game update. A pass for thread safety of several subsystems was performed, including the attention target component and communication system. This is required to eventually move the Subsumption component update to the multithreaded batch update step.
In FPS Combat, the ‘Defend Area’ assignment was introduced; correctly achieving this behavior requires monitoring the mastergraph transitions to evaluate if the recipients of the Subsumption event can actually process it. In the Defend Area example, they might be executing any regular behavior when receiving the assignment. If the behavior can handle the request in a specific way, great. If not, then the mastergraph takes care of selecting one that can. Alongside this, they’re adding new behaviors to improve combat and patrol to respect this assignment.
New behaviors and functionality to support stealth gameplay were implemented, with new audio and visual stimuli being added to allow players to draw the attention of guards, prepare traps, and open up otherwise blocked paths.
Work also continued on the bartender for Lorville. To achieve several functionalities of his behavior, they implemented the first pass of UseChannel routing and are continuing to expand the usable functionalities.
The Usable Builder Tool received a new feature too: it’s now able to correctly preview different characters using different usables so that designers, animators, and programmers can easily test and verify the content as it’s delivered.
Animation
On the Story front, the Animation kicked-off production passes on a handful of Squadron 42 scenes. They’re also working to finalize the Armorer character for SQ42 – itself a large and intricate task.
Audio
Audio worked closely with the SQ42 composer Geoff Zanelli to establish themes for the game’s different races and important characters. This, combined with the second round of music implementation, allowed the team to better support pacing and overall development.
The Dialogue Team worked to ensure animation and design had all the assets required to successfully implement their conversations, comms, and cinematics.
Character Art
The Character Art Team polished the Vanduul armor and concepted the Navy Gunner’s outfit.
Cinematics
After completing the CitizenCon SQ42 teaser trailer, Cinematics took time to verify that each scene was functioning correctly from start to finish. This mainly involved the Shubin Station art pocket, but also other things like the battleground around Vega II. Once complete, they worked on a pivotal scene for the game featuring a key character not revealed yet. This involved using a new method of character hair and skin creation (tweaked for more realism), and small modification to costumes.
The Cinematic Animation Team carried on with regular scene work. Having completed first passes for much of the game’s narrative, they transitioned to scenes where a full implementation pass with a state machine is required. They also supported the engineers working on key workflow tools.
Along with navspline improvements, new functionality was added to allow the team to edit multiple cinematic sequences at once. Previously, TrackView only supported a master and child sequence and didn’t allow editing of the master if the child was edited, or vice versa. Some SQ42 scenes feature characters on capital ship bridges reacting to things they see through windows, which requires the team to split sequences between interior and exterior. The new multi-sequence workflow allows multiple sequences to be open and active at once and syncs the timelines for both the master and child.
Engine Tools
The Engine Team resumed work on GPU skinning. They added vertex velocity support (motion blur), completed several optimizations to skip zero weights (improved throughput), prepared background data, and made the first pass on memory layout and LOD support.
They also made the execution of ray collision checks and the defragmentation of grids run concurrently. This achieved a 30-50% speedup for physics planet terrain computation, reduced the number of cell queries on planets, and improved proxy mesh generation of terrain ground volumes.
Terrain rendering improvements were added (glow forward pass) as well as fixes for water volume and ocean rendering. The existing hair shader was improved, and a new depth of field algorithm was created to improve quality, performance, and fix halos around silhouettes.
Part of the team worked on additional culling refinements in the zone system to submit fewer objects to the renderer, as well as various low-level optimizations to reduce load on the render thread.
Engineering
Engineering actualized a system to allow variable limits on how far players can move their heads when looking around. The default amount is overridden by the outfit and helmet, so wearing heavy armor will restrict how far they can look.
Pickup and Carry was finished off, including the solving of an issue when interacting with items in EVA.
Developments on the female character continues. Because of her different sized skeleton, the team implemented animation-driven inverse kinematics to allow her to reach a ship’s controls without the need for new animation sets.
Progress has been made on the usables builder tool, which allows the content creators to drop in a character and play all the related usable animations, move locators around, and generally test a setup without having to go into the game.
As part of comms, a ‘Tannoy’ system can now pump audio to multiple parts of an environment. For example, an announcement to a single ship’s hangar or a more global ship-wide announcement.
The ship AI Team helped out with the new Intelligent Flight Control System (IFCS), tweaking ship behavior to better utilize these new flight controls for a better dogfighting experience.
Environment Art
Art began using their new hard surface shader and new blending features for wear and tear. This enables a more realistic appearance of localized damage without a jarring transition between worn and pristine areas. They’re paying particular attention to make sure wear looks natural and unforced. One of the high-level goals for SQ42 is for every asset and its features to sit in a scene naturally, feel unforced, and for the lighting to have a slightly softer, more realistic feel (except for some areas where the intensity is cranked up to 11).
Lighting focused on the Javelin found in an early campaign level, taking into account the emphasis on making one key light do more of the work. This new approach looks great and is less demanding on the engine too. Tweaks to a control room seen close to the end of the campaign progressed, with the aim being to set the correct tone for the narrative and gameplay moments that spread from it.
Props seen throughout the campaign (including monitors, screens, wiring looms, hatch covers, ropes, destructible lights, and pressurized items) all received attention, this time to determine how they break or deform when damaged. Several key events take place where these assets need to react correctly to gravity, decompression, damage, pulse, etc.
The vast Shubin mining station gained more detail to the supporting structures around it. Development of the facility’s Bridge (as first seen in the CitizenCon 2948 trailer) continued, which comes in at around three times the size of a Bengal’s.
Gameplay Story
The Gameplay Story Team made swift progress throughout November and continuously added more scenes to their Q4 list. They are currently working on 38 scenes for the quarter and are expecting to add several more by the end of the year.
Graphics
The Graphics Team worked on several shader effects, including the resurrection of the caustics water effect, which is needed in several locations throughout SQ42. The new hard surface shader was rolled out to the entire team and should improve performance, allow new surface shading features, and enable more dynamic wear & dirt effects.
Performance was also a focus, with most attention on the low-level texture and mesh streaming systems to help squeeze as much content in with as little performance impact as possible.
Level Design
The Level Design Team converted the older sables inside the Idris to a more efficient and flexible system, which also incorporates crew behaviors for things like ‘off-duty’ and ‘mess hall’. Level work is an ongoing collaboration with the Art Team and is constantly reviewed at senior level.
“It’s all going well and now that we have almost all the scenes in the levels you really get a great feel for the story flow and pacing.”
Cockpit scenes are coming to life thanks to ‘Render to Texture’ technology, while the new IFCS system is fully implemented into SQ42 and making a huge difference to dogfighting. Regular feedback and suggested improvements mean spline technology and flight controls are constantly refined.
Narrative
The Narrative Team continued plugging away at [REDACTED] [REDACTED] [REDACTED] [REDACTED] as well as [REDACTED] [REDACTED] [REDACTED] and that was a lot of fun.
Props
The Props Team continued work on the assets required for NPS interactions and activities by creating additional sub items used by the engineering crew and the storage cases to house them. The larger maintenance machinery assets are now ready for the animation and cinematic departments to use in their work, too.
System Design
The System Design Team integrated the New Flight Model into enemy ship AI, ensuring that they are still engaging to fight against and don’t become unbalanced. They noticed that the new IFCS currently causes too much unwanted ‘jousting’ behavior, so are currently looking into ways to modify it.
Dialogue wildlines for the ship/FPS/social AI were reworked to unify them within the same overall structure. Collaboration with the audio & writing teams ensured the system works properly for all systemic dialogue in the game. The team is also working to develop tools to automate the setup of dialogue lines.
Stealth gameplay elements continue to be developed, which require the AI perception to be upgraded to cater for peripheral vision, as well as various audio events and stimuli from environmental sources, such as throwing a pebble to distract enemies.
Tech Animation
The Technical Animation department progressed with the initial batch transfer of male animations to the female skeleton. This included updating low-level assets for animation database referencing to ensure she can run around and fire weapons. It has been successful and handed off to animation for further review and polish.
Some much-needed toolsets for authoring skinning data on the many different costumes were finished. Used in conjunction with the existing toolsets, these will make skin authoring a more efficient process.
An interesting dilemma was presented recently, whereby the team needed to show some sort of fluid dynamics, which usually require intensive calculations The Technical Animation department came into its own and used the existing physics solution to create a dynamic yet economic fake for the various glasses & cups in the bar scenes.
Multiple animations for cinematics and gameplay were added, as were several new tools to the animation pipeline along with bug fixes and additions to existing tools. Time was also spent fixing several smaller bugs like animation compilation errors, missing integrations, weapon entities, and DBA setups.
Tech Art
The Tech Art Team analyzed the full requirements of the character ‘DNA gene pool’. In order for the next-gen facial customizer to work most effectively, a limited pool of heads with specific and unique shapes is required. Relevant factors are gender, ethnic origin, age, physical constitution, and distinct facial features such as hooked vs. pointy nose, thin vs. full lips, and so forth. Several scenarios with varying pool sizes were created to determine the mid-to-long-term plans for populating the pool. The planned release of the new customizer will initially use as many heads as possible from the selection scanned, providing they fulfill requirements.
The team also worked on the asset authoring tools and pipeline for the new cloth/softbody solver, which was first showcased at CitizenCon. Optimal simulation mesh topology and vertex density are key to making it work efficiently and fast enough while yielding high-fidelity visual results. Another important factor is creating the best possible binding between the high and low res simulation mesh – this can only be fully automated for simpler cloth asset types and requires artistic ‘guidance’ and fine-grained control in more complex cases. The team went to great lengths to ensure the authoring tools provide this capability in a convenient, easy-to-use way.
UI
Last month, the SQ42 team specced-out improvements to how AR mission objectives are displayed to the player. For both the PU and SQ42, they’re aiming to create a common unified methodology for how important information is imparted regarding type, position, whether it’s obstructed, etc. They’re also looking at the long-term requirements of missions and building a system to help to surface important information when it’s contextually needed.
Another major feature worked on is the area map. Pre-visualizations of how the map could be were built procedurally using existing underlying systems, such as the room system. This informs not only the overall layout but also how it becomes more defined as the player traverses the environment for the first time.
Vehicle Features
The team spent the month on Vehicle Scanning improvements. The groundwork necessary to allow ships to aim at the engines on target ships has been completed, and the feature itself is nearly ready to be rolled out. Scanning nav points for destination info have been completed and are also ready for implementation.
VFX
VFX continued to iterate on lightning effects by putting the new texture noise functionality through its paces, which will allow them to create much finer detail up close at a fraction of the previous cost. They also developed a tool to allow artists to create VDBs (including gas clouds) more quickly and with more control over the finer details.
Thruster improvements were made to more closely match the VFX. They gained new effects and functionality including damage, overheat, and misfire options.
R&D for a Xi’an missile launcher kicked off too.
Weapons
The Weapon Art Team carried on with the Multi-Tool rework and made progress with the Kastak Arms Ravager-212 and the level two and three upgrades for the Hurston Dynamics Laser Repeaters. They also made minor adjustments to the iron sights on a handful of weapons to improve the sight picture and to make them more user-friendly when no optics are attached.
Covert Intel
Conclusion
WE’LL SEE YOU NEXT MONTH…
$(function() { Page.init();
window.Page = new RSI.Game.About(); });
Source: https://robertsspaceindustries.com/comm-link/transmission/16919-Squadron-42-Monthly-Report-December-2018







